It inhibits action potentials by increasing the stimulus required to move the membrane potential to the action potential threshold. Describe the distribution of ions insideoutside of the cell.
What Happens When The Cell Undergoes Hyperpolarization Quora
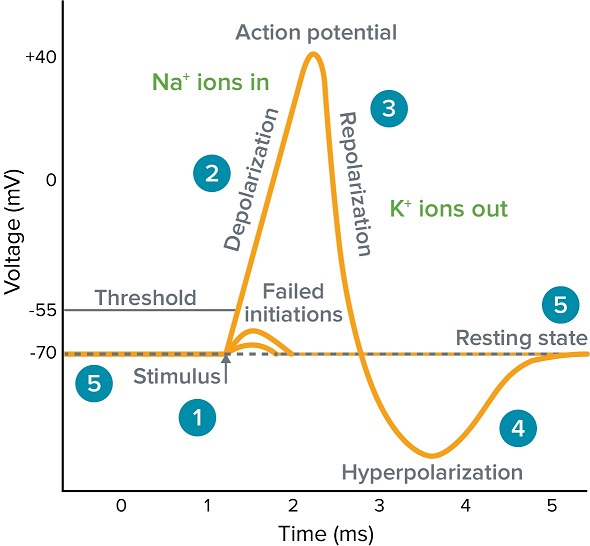
Prior to hyperpolarization and in the first stage of an action potential we have depolarization.

. Describe the difference in the function of hyperpolarization in action potentials vs. On the other hand. That is hyperpolarization is an increase in the absolute value of a cells membrane potential.
Describe the molecular events that generate the dark current in photoreceptor cells. Hyperpolarization depolarization and repolarization of a neuron are all caused by the flow of ions or charged molecules in and out of the cell. Hyperpolarization is measured either as an increased outward current or decreased inward current.
Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K through K channels or influx of Cl through Cl channels. It is the opposite of a depolarization. Overview of the functions of the cerebral cortex.
Saltatory conduction in neurons. Hyperpolarization is a change in a cells membrane potential that makes it more negative. Na stops flowing into the cell.
Describe the phenomena of depolarization repolarization and hyperpolarization in reference to the resting membrane potential. Thus any change of membrane voltage in which the membrane potential moves farther from zero in either a positive or negative direction is a hyperpolarization. This structure is generally referred to as the phospholipid bilayer.
Membrane approached -50mv the K gates open slow acting till reach 30mv as K flows out of the cell begins Repolarization. This is the currently selected item. The temporary hyperpolarization of a membrane.
Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential caused by somatostatin in dissociated human pituitary adenoma cells that secrete growth hormone. The sodium potassium pump corrects the location of Na and k. Hyperpolarization is the opposite of the depolarization.
It is the opposite of a depolarization. When added to cells maintained at resting membrane potential Step 1 amiodarone intercalates into the bilayer and may alter lipid fluidity resulting in membrane hyperpolarization Step 2. It is the opposite of a depolarization.
Depolarizationa decrease in negative chargeconstitutes an excitatory PSP because if the neuron reaches the critical threshold potential it can excite. A biological membrane biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartmentsBiological membranes in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded integral and peripheral proteins used in communication. In addition to the various types of lipids that occur in biological membranes membrane proteins and sugars are also key components of the structure.
It is the opposite of a depolarization. The cell body receives messages from other cells which. The membrane potential is maintained by a voltage clamp and amplifier this voltage clamp is then able to measure small current flow changes.
An ISEV position paper arising from the ISEV membranes and EVs workshop J Extracell Vesicles. Excitatory postsynaptic Potential EPSP Definition. Since it increases the negative charge outside the membrane the initiation of an action potential is prevented by hyperpolarization.
Hyperpolarization is any change in a cells membrane potential that makes it more polarized. Electrotonic and action potentials. Can action potentials regenerate along the axon membrane between the nodes of ranvier.
Neuron depolarization hyperpolarization and action potentials. Hyperpolarization in graded potentials Hyperpolarization is a change in a cells membrane potential that makes it more negative. Hyperpolarization is a change in the membrane potential of a cell to a greater negative value that implies that there is moving further away from zero.
At higher doses the membrane depolarizes as calcium and protons rush into the cytosol Step 3 disrupting ion homeostasis and leading to cell death. Biological membranes in EV biogenesis stability uptake and cargo transfer. Hyperpolarization can be caused for instance by opening channels that allow positive ions to move out of the cell or negative ions to move in.
Briefly describe the Fluid Mosaic model of bio-membranes Jonathan Singer and Garth Nicholson proposed the Fluid Mosaic Model of Biological membranes Biological membrane can be viewed as Two-dimensional solutions of oriented Lipids and Globular proteins Integral membrane proteins can be considered as. Hyperpolarizationthat is an increase in negative charge on the inside of the neuronconstitutes an inhibitory PSP because it inhibits the neuron from firing an impulse. Neuronal synapses chemical The synapse.
Electrochemical processes are generally responsible for the occurrence of hyperpolarization across cellular membranes. Describe the phenomena of depolarization repolarization and hyperpolarization in reference to the resting membrane potential. When a cell is at rest these ion channels remain closed however when the membrane potential reaches a certain point called the threshold potential they open.
Hyperpolarization refers to an increase in the amount of the electrical charge making the resting membrane potential more negative. Explain the impact of this cycle on the typical resting membrane potential and how light leads to a hyperpolarization of the membrane. Hyperpolarization is when the difference in electrical potential between two sides of a cellular membrane changes significantly resulting in a large electrical potential across the membrane.
Biological membranes consist of a double sheet known as a bilayer of lipid molecules. Occurs and the cell membrane reaches -90mv. Hyperpolarization is a change in a cells membrane potential that makes it more negative.

Hyperpolarization Definition Summary Epilepsy Facts
Why Does Hyperpolarization Occur Why Does The Membrane Potential Go Past The Resting Potential Quora
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices
0 Comments